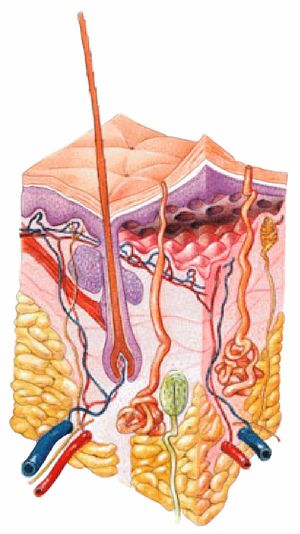
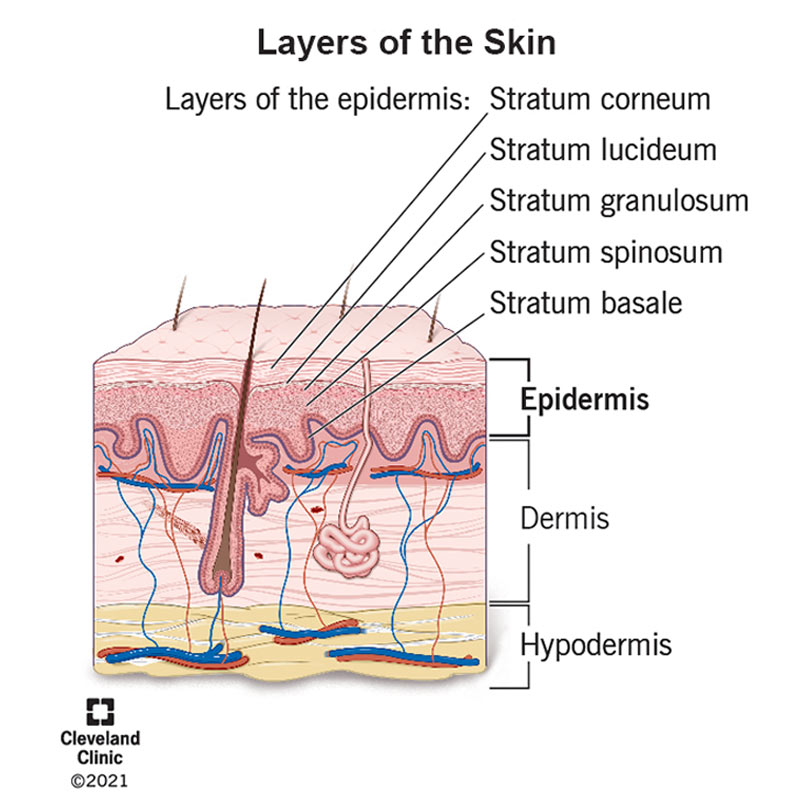
Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane 7 Functions: 1. Protective covering 2. Regulates body temperature 3. Manufactures Vitamin D 4. Sensory function. - ppt download

Stromal Cells Covering Omental Fat-Associated Lymphoid Clusters Trigger Formation of Neutrophil Aggregates to Capture Peritoneal Contaminants - ScienceDirect

Health Science 1. Structure of the Skin Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane 3 layers Epidermis Outermost covering Epithelial cells Avascular-no blood. - ppt download
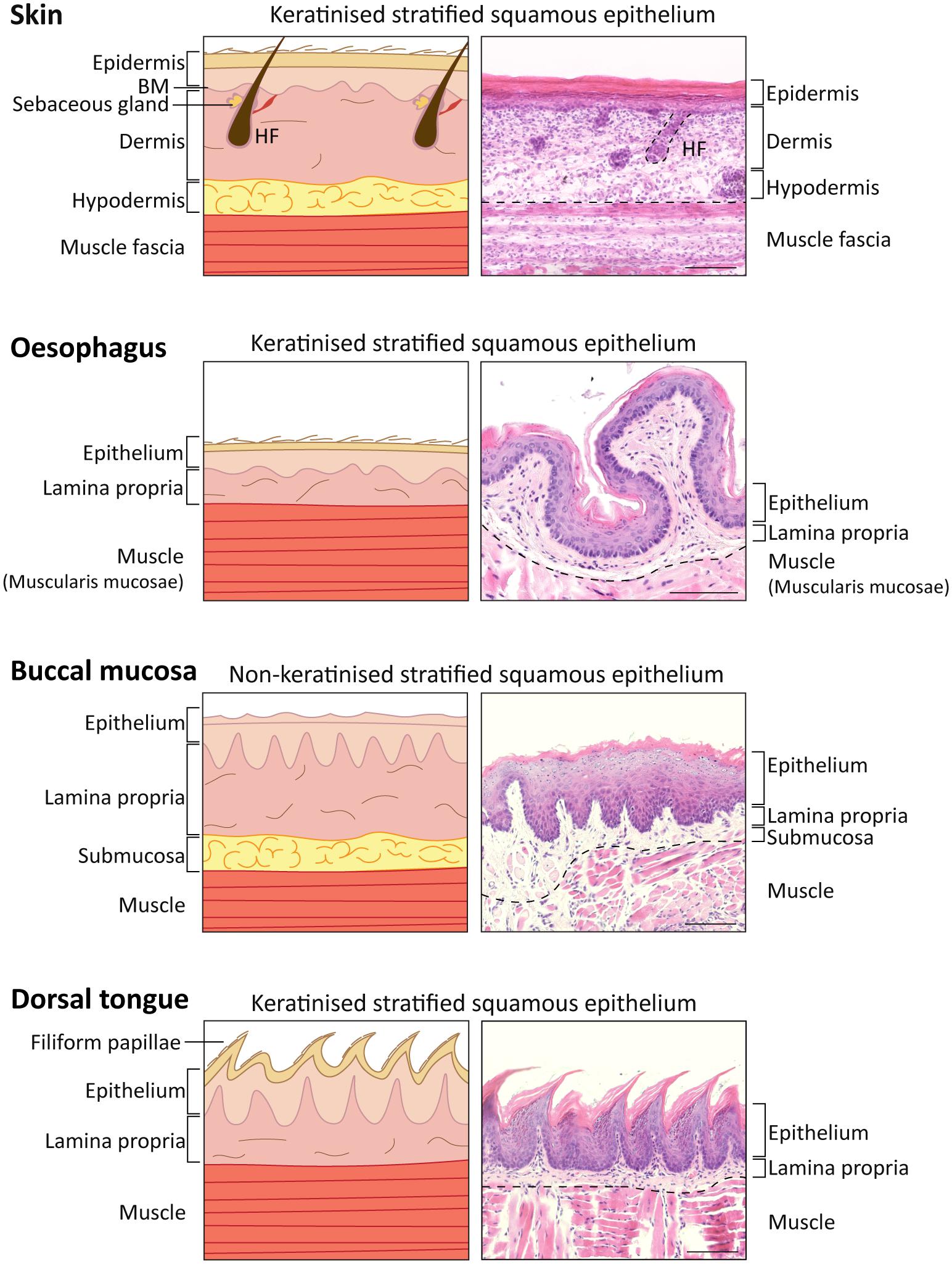
Frontiers | A Scarless Healing Tale: Comparing Homeostasis and Wound Healing of Oral Mucosa With Skin and Oesophagus

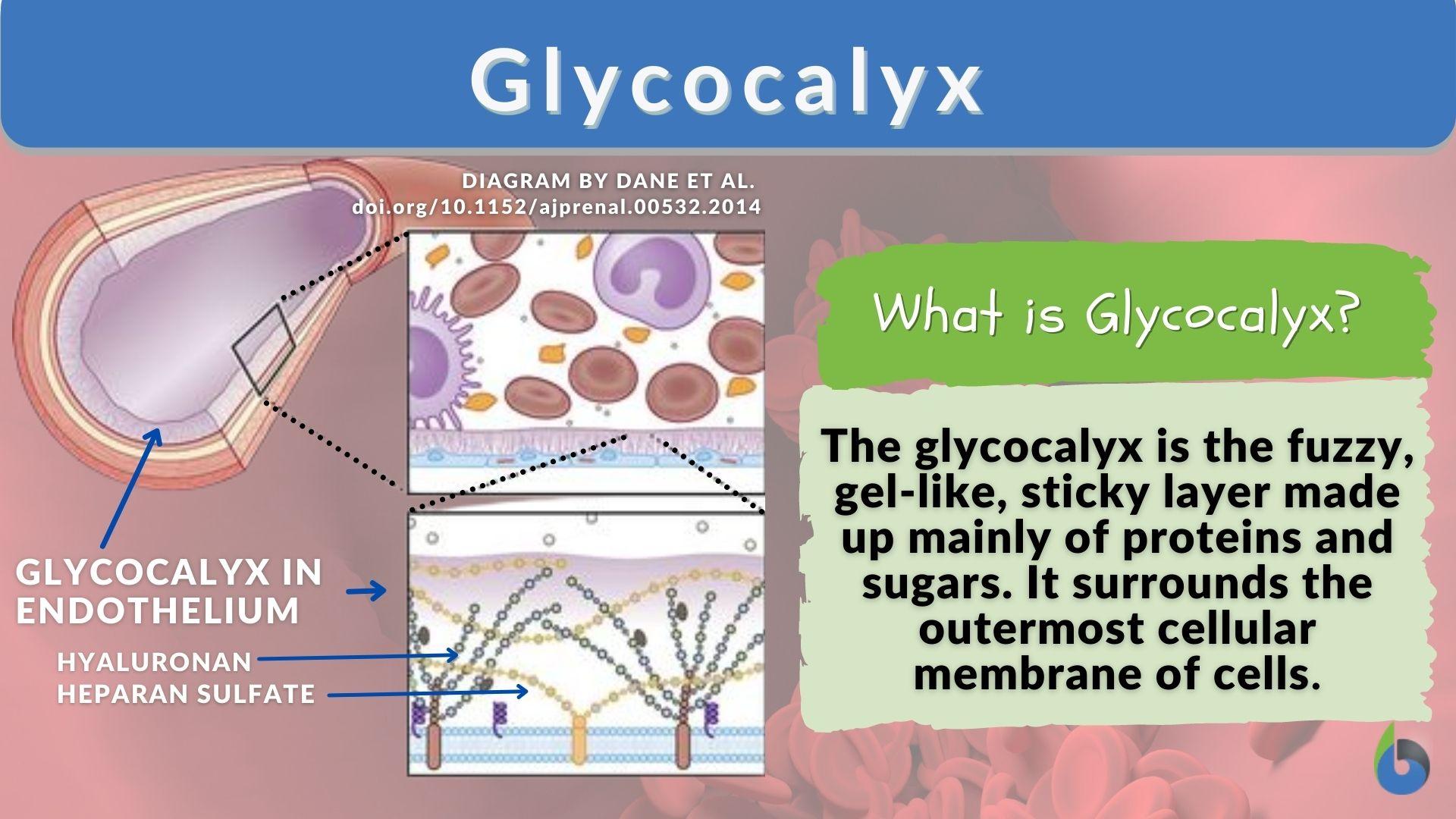
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/anatomy-of-the-brain--meninges--hypothalamus-and-anterior-pituitary--1134486874-240d1e77d3364d5b8572be4b44a43666.jpg)

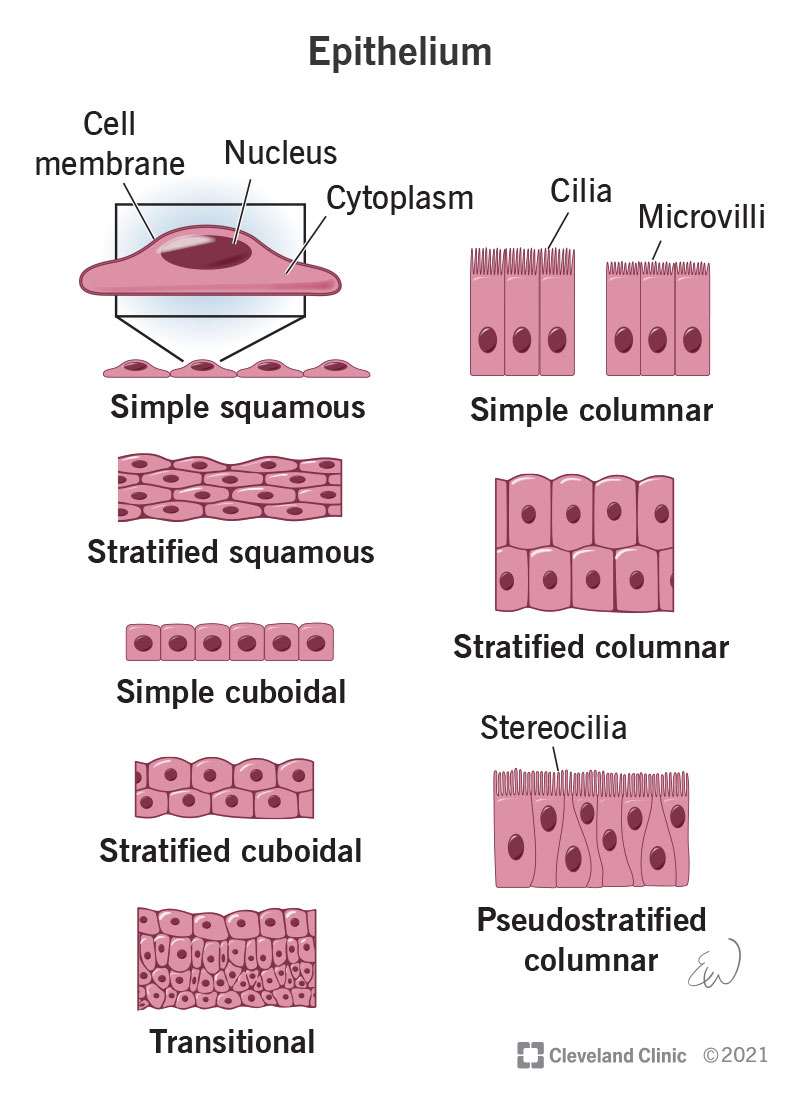

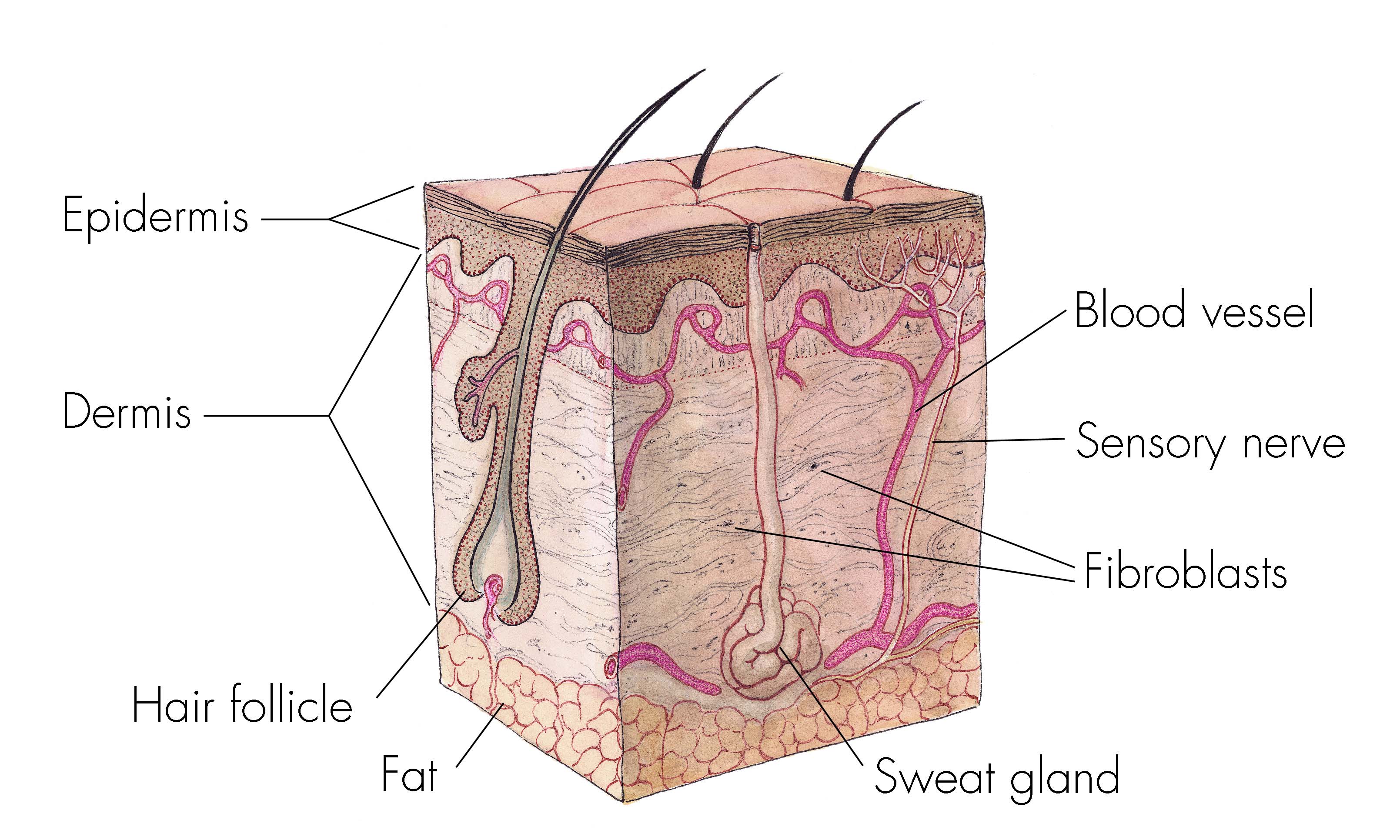


:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/skin-3/h6G3JZ3UBPkaVcwo8735yA_1Skin.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/skin-anatomy-1068880_review-01-9adf9daebac8464eb693274a960bd850-52cb9a92cd394931afe6abfca8074e28.png)